Insurance: Understanding Its Definition, Types, and Benefits
Insurance is a vital tool for managing risk and securing financial stability. It provides a safety net against unforeseen events, ensuring that individuals and businesses can recover from unexpected losses. In this article, we will explore the definition of insurance, how it works, its common types, benefits, and the main purpose it serves.
What is Insurance?
Insurance is a legal contract between an individual or entity (policyholder) and an insurance company (insurer). The insurer agrees to provide financial compensation for specified losses or damages in exchange for regular payments known as premiums. This arrangement allows individuals to transfer potential financial risks to the insurance company, thereby mitigating the impact of unexpected events.
How Does Insurance Work?
Insurance operates on the principle of risk transfer. Policyholders pay premiums to the insurer, who pools these funds to cover the losses of a few policyholders. This system allows individuals to manage risks that might otherwise be financially devastating[3][8]. When a policyholder experiences a covered loss, the insurer pays out according to the terms of the policy, helping the policyholder recover financially.
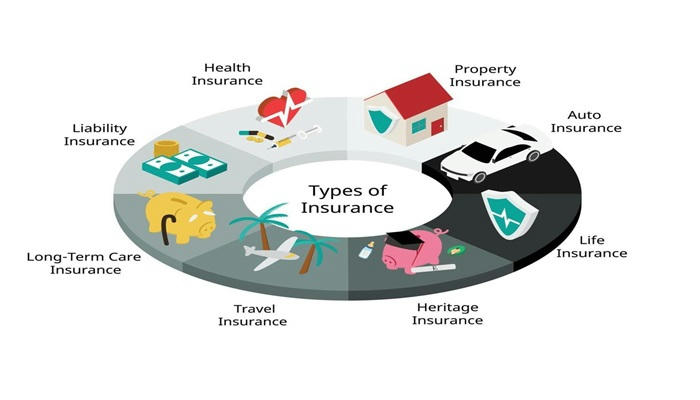
What Are the Most Common Types of Insurance?
- Life Insurance: Provides a death benefit to beneficiaries upon the policyholder's passing. It can be whole life or term life, offering financial security for dependents.
- Health Insurance: Covers medical expenses, protecting against high healthcare costs due to illness or injury.
- Auto Insurance: Protects against financial losses resulting from vehicle accidents or damage.
- Long-Term Disability Insurance: Ensures income replacement if an individual becomes unable to work due to illness or injury.
- Property Insurance: Covers damage to homes or businesses from events like natural disasters or theft.
What Are the Benefits of Taking Out Insurance?
Insurance offers several benefits:
- Financial Protection: Provides a safety net against unexpected expenses, ensuring financial stability.
- Peace of Mind: Reduces stress by knowing that you have coverage in case of emergencies.
- Risk Mitigation: Transfers potential financial burdens to the insurer, allowing you to manage risks more effectively.
- Long-Term Wealth Creation: Some insurance plans, like whole life insurance, can accumulate cash value over time.
- Tax Benefits: Certain insurance policies may offer tax advantages, such as deductions on premiums.
What is the Main Purpose of Insurance?
The primary purpose of insurance is to provide financial security and stability by mitigating risks associated with unforeseen events. It ensures that individuals and businesses can recover from losses without facing financial ruin.
What Are the 5 Benefits of Insurance?
- Financial Stability: Ensures that you can cover expenses even in adverse circumstances.
- Peace of Mind: Offers reassurance that you are protected against unexpected events.
- Risk Management: Allows you to manage risks more effectively by transferring them to the insurer.
- Long-Term Wealth Creation: Some insurance plans can help build wealth over time.
- Tax Advantages: May provide tax benefits, such as deductions on premiums.

What Risks Are Not Covered by Insurance?
Certain risks are considered uninsurable due to their high probability of occurrence or the potential for catastrophic losses. Examples include reputational risk, regulatory risk, and pandemic risk. Additionally, risks resulting from illegal activities or willful acts are typically not covered.
Who Bears Risk in Insurance?
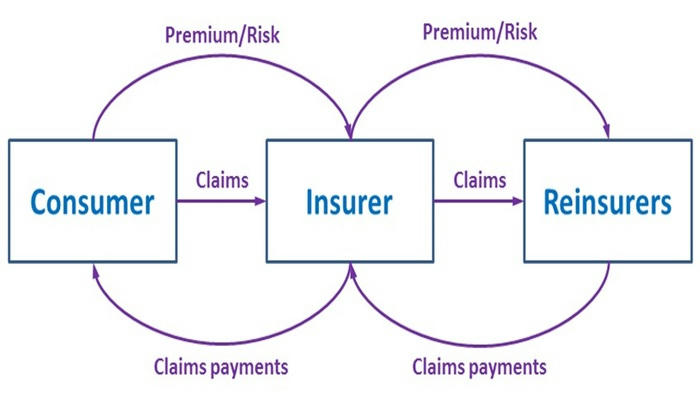
In insurance, the risk is transferred from the policyholder to the insurance company. The insurer bears the risk by agreeing to pay for covered losses in exchange for premiums[6][8]. However, insurance companies can further transfer some of this risk to reinsurers to manage their own exposure.